Plasmids
From Markus Heitzer, University of Regensburg-Germany, November 2007
codon-adapted Gaussia princes luciferase under control of HSP70A/RBCS2 promoter
host strain: Pir1 (Invitrogen)
kanamycin resistant
Fuhrmann M, Hausherr A, Ferbitz L, Schödl T, Heitzer M, Hegemann P (2004) Monitoring dynamic expression of nuclear genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a synthetic luciferase reporter gene. Plant Mol Biol 55:869-881 Heitzer M, Zschoernig B (2007) Construction of modular tandem expression vectors for the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using the Cre/lox-system. Biotechniques 43:324
From Markus Heitzer, University of Regensburg-Germany, November 2007
loxP, HSP70A/RBCS2 promoter, codon-adapted human erythropoietin with ARS2 leader and RBCS2 introns, His6 tag, RBCS2 3′ UTR
host strain: Pir1 (Invitrogen)
kanamycin resistant
Fuhrmann M, Hausherr A, Ferbitz L, Schödl T, Heitzer M, Hegemann P (2004) Monitoring dynamic expression of nuclear genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a synthetic luciferase reporter gene. Plant Mol Biol 55:869-881 Heitzer M, Zschoernig B (2007) Construction of modular tandem expression vectors for the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using the Cre/lox-system. Biotechniques 43:324
pAES14 Renilla luciferase
$30.00
$30.00
From Markus Heitzer, University of Regensburg-Germany, November 2007
ARS2 promoter, codon-adapted crluc Renilla luciferase with RBCS2 introns, Hs6 tag; kanamycin resistant
host strain: Pir1 (Invitrogen)
kanamycin resistant
Fuhrmann M, Hausherr A, Ferbitz L, Schödl T, Heitzer M, Hegemann P (2004) Monitoring dynamic expression of nuclear genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a synthetic luciferase reporter gene. Plant Mol Biol 55:869-881
pUC-Arg7-lox-B ARG7 genomic
$30.00
$30.00
From Markus Heitzer, University of Regensburg-Germany, November 2007
ARG7.8 genomic sequence inserted into pUCBM20, followed by loxP site
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
Heitzer M, Zschoernig B (2007) Construction of modular tandem expression vectors for the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using the Cre/lox-system. Biotechniques 43:324
pKS-aphVIII-lox aphVIII
$30.00
$30.00
From Markus Heitzer, University of Regensburg-Germany, November 2007
expression vector containing loxP, beta-tubulin promoter, aphVIII, and 3′ UTR from chlamyopsin-1
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
Heitzer M, Zschoernig B (2007) Construction of modular tandem expression vectors for the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using the Cre/lox-system. Biotechniques 43:324
pKS-aph7“-lox aph7
$30.00
$30.00
From Markus Heitzer, University of Regensburg-Germany, November 2007
Expression vector containing loxP, beta-tubulin promoter, aph7 with intron 1 from RBCS2, and 3′ UTR from chlamyopsin-1
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
Heitzer M, Zschoernig B (2007) Construction of modular tandem expression vectors for the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii using the Cre/lox-system. Biotechniques 43:324
pGenD PSAD cassette
$30.00
$30.00
PSAD gene, from which coding region can be removed and replaced with a gene of interest under control of the PSAD flanking sequences
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
Fischer N, Rochaix JD (2001) The flanking regions of PsaD drive efficient gene expression in the nucleus of the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Gen Genet 265:888-894
pBACmn
$30.00
$30.00
From Pete Lefebvre, University of Minnesota
plasmid used in preparing the BAC library
chloramphenicol resistant
pGwyCrRNAi:fwd
$30.00
$30.00
From Xingshan Jiang, David Stern lab, Boyce Thompson Institute, August 2008
Gateway derivative of Maa7/XIR
amp resistant
pGwyCrRNAi:rev
$30.00
$30.00
From Xingshan Jiang, David Stern lab, Boyce Thompson Institute, August 2008
Gateway derivative of Maa7/XIR
amp resistant
pJK7
$30.00
$30.00
Herbicide resistant ALS gene
This plasmid can be used as a dominant selectable marker on sulfometuron methyl (SMM) in Chlamydomonas and confers ampicillin resistance in E. coli.
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
Kovar JL, Zhang J, Funke RP, Weeks DP (2002) Molecular analysis of the acetolactate synthase gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and development of a genetically engineered gene as a dominant selectable marker for genetic transformation. Plant Journal 29:109–117
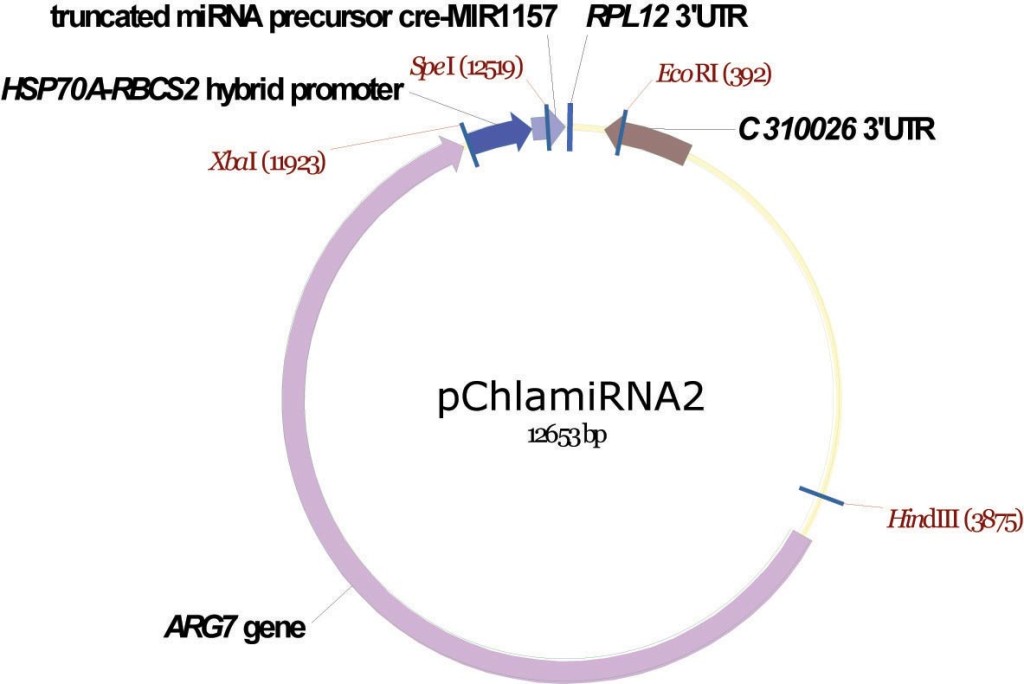
pChlamiRNA2
$30.00
$30.00
From Attila Molnar, David Baulcombe lab, University of Cambridge, December 2008
Artificial mRNAi construct
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
Molnar A, Bassett A, Thuenemann E, Schwach F, Karkare S, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Baulcombe D (2009) Highly specific gene silencing by artificial microRNAs in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 58:165-174
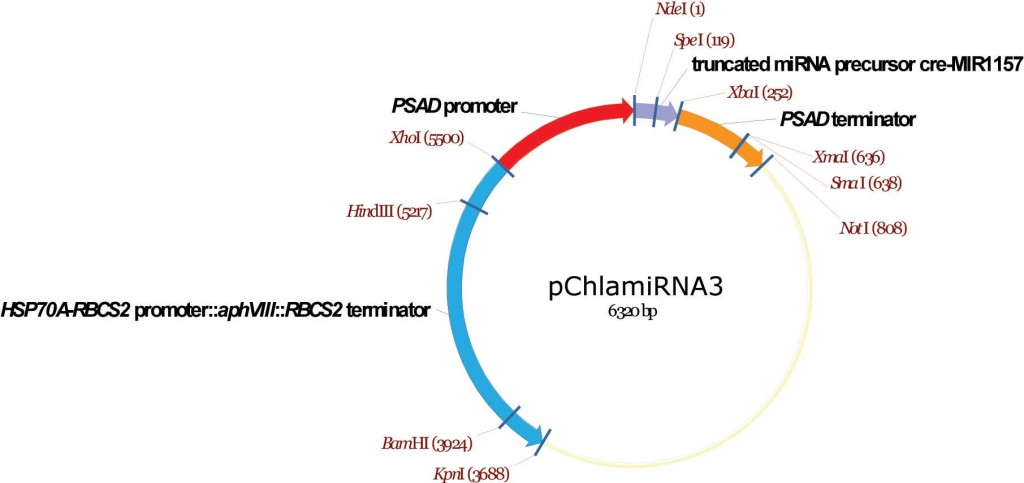
pChlamiRNA3
$30.00
$30.00
From Attila Molnar, David Baulcombe lab, University of Cambridge, December 2008
Artificial mRNAi construct
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
Molnar A, Bassett A, Thuenemann E, Schwach F, Karkare S, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Baulcombe D (2009) Highly specific gene silencing by artificial microRNAs in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 58:165-174
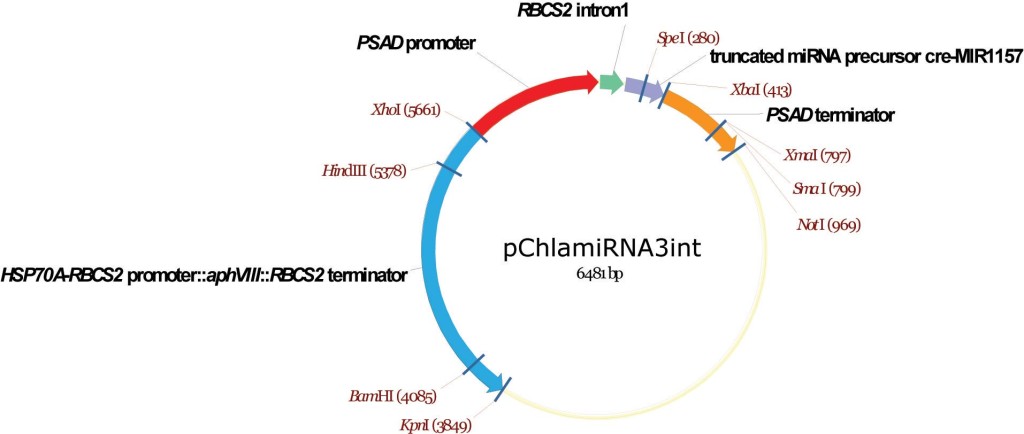
pChlamiRNA3int
$30.00
$30.00
From Attila Molnar, David Baulcombe lab, University of Cambridge, December 2008
Artificial mRNAi construct
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
Molnar A, Bassett A, Thuenemann E, Schwach F, Karkare S, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Baulcombe D (2009) Highly specific gene silencing by artificial microRNAs in the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant J 58:165-174
From Dudley Page, Merchant lab, UCLA, March 2009
This plasmid is a Gateway-adapted form of the arylsulfatase reporter vector pJD100.
host strain: Survival T1 (Invitrogen)
amp resistant
Allen MD, Kropat J, Merchant SS (2008) Regulation and localization of isoforms of the aerobic oxidative cyclase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Photochem Photobiol 84:1336-42
pHyg3
$30.00
$30.00
From Wolfgang Mages, University of Regensburg, November 2009
Hygromycin resistance vector
host strain: DH5 alpha
ampicillin resistant in E. coli
Berthold et al. 2002. Protist, Vol. 153, 401–412
pHyg4
$30.00
$30.00
From Wolfgang Mages, University of Regensburg, November 2009
Hygromycin resistance vector
This plasmid is almost identical pHyg3, only the rbcS2 intron1-sequence is absent in pHyg4. The pHyg4 sequence could easily be made by deleting the intron sequence from pHyg3.
host strain: DH5 alpha
ampicillin resistant in E. coli
pMS188
$30.00
$30.00
From Michael Schroda, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, August 2010
ble gene behind HSP70A-RBCS2 promoter
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
pMS539
$30.00
$30.00
From Michael Schroda, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, August 2010
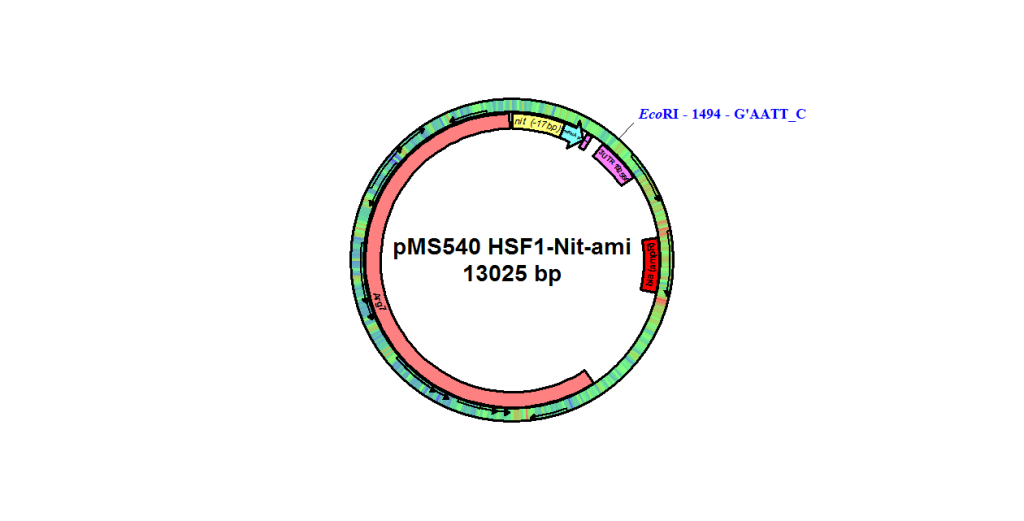
NIT1, amiRNA, RPL12 UTR, C_310026 UTR
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
pCB720
$30.00
$30.00
From Michael Schroda, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, via Lai-Wa Tam, U of MN, August 2010
HSP70B gene behind HSP70A promoter
host strain: DH10B
amp resistant
pCB740
$30.00
$30.00
From Michael Schroda, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, via Lai-Wa Tam, U of MN, August 2010
HSP70B gene behind HSP70A-RBCS2 promoter
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
pCB801
$30.00
$30.00
From Michael Schroda, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, via Lai-Wa Tam, U of MN, August 2010
aadA gene behind HSP70A-RBCS2 promoter, 3’RBCS2
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
pMS540
$30.00
$30.00
From Michael Schroda, Max Planck Institute of Molecular Plant Physiology, October 2010
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
pSS1
$30.00
$30.00
From Robert Spreitzer, Univ. of Nebraska, May 2011
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
pSL72
$30.00
$30.00
From Wenqiang Yang, Carnegie Institution, Grossman Lab, July 2011
The psaD promoter is cloned between KpnI and XhoI, and the psaD terminator between XbaI and NotI. This promoter drives the expression of the AphVIII coding sequence cloned between NdeI and EcoRV.
host strain: DH5 alpha
amp resistant
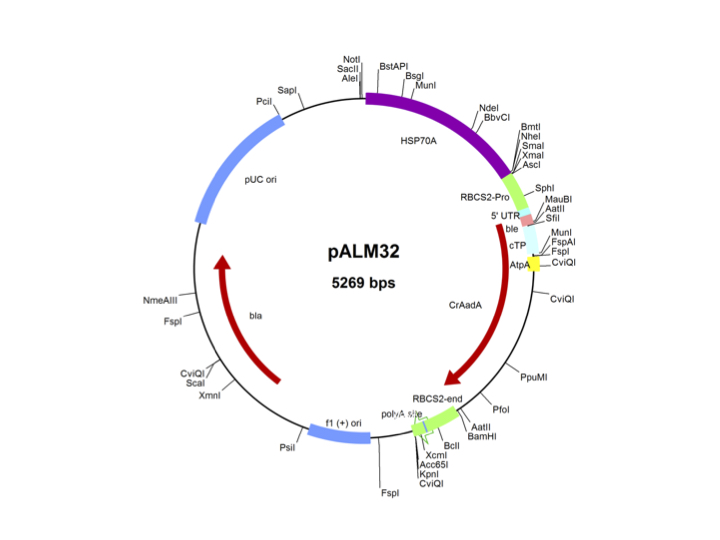
pALM32
$30.00
$30.00
Source: Olivier Vallon, Institut de Biologie Physico-Chimique, Paris, November 2011
Used for insertional mutagenesis, complementation by cloned genomic fragments
Insert: CrAadA (AR promoter, RBCS2 3′-UTR)
Origin: CrAadA into pMS188 (AatII)
Vector: Bluescript
Host strain: DH5α
Ap resistant
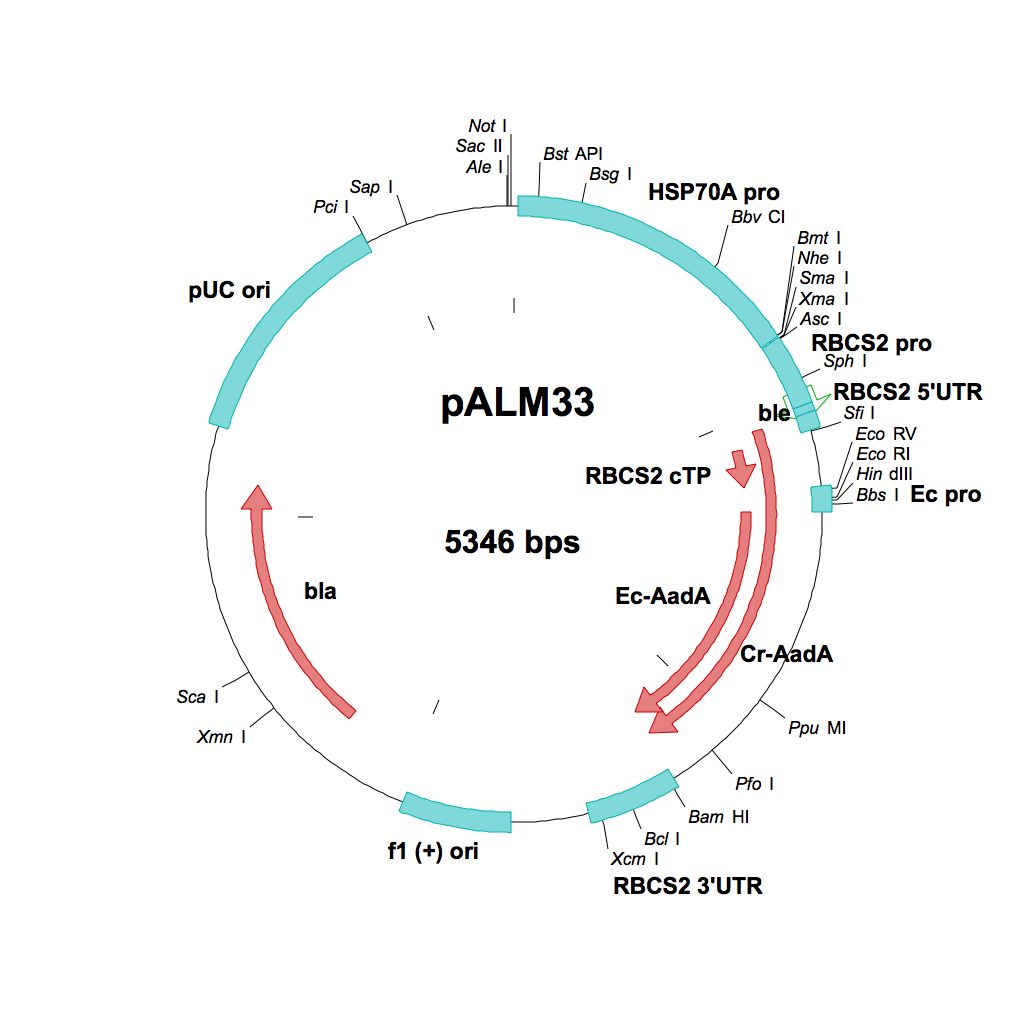
pALM33
$30.00
$30.00
Source: Olivier Vallon, Institut de Biologie Physico-Chimique, Paris, November 2011
Used for insertional mutagenesis, marker rescue
Insert: CrSpAadA (AR promoter, RBCS2 3′-UTR)
Origin: E. coli artificial promoter into pALM32 (FspAI)
Vector: Bluescript
Host strain: DH5α
Ap Sp resistant
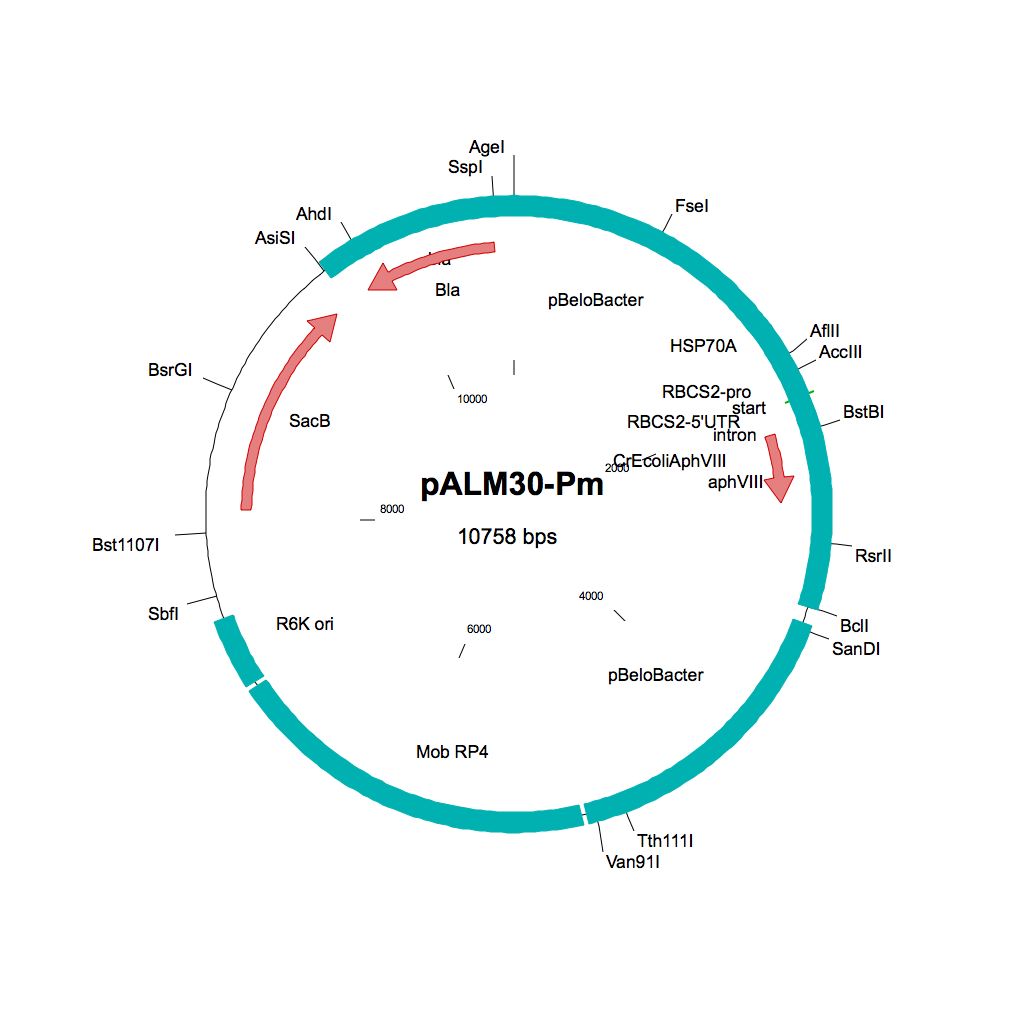
pALM30-Pm
$30.00
$30.00
Source: Olivier Vallon, Institut de Biologie Physico-Chimique, Paris, November 2011
Used to modify Chlamydomonas genomic BACs to Pm resistance
Insert: AphVIII (AR promoter, RBCS2 3′-UTR)
Origin: pCVD442 with IS1 and CmR removed (NdeI AsiSI) and replaced by bla, then inserting 3 kbp of pBeloBAC11-Nit8 (AscI AgeI), then inserting (FseI) the AphVIII marker from pBC1
Vector: R6K
Host strain: S17-1 λpir
Ap Pm resistant
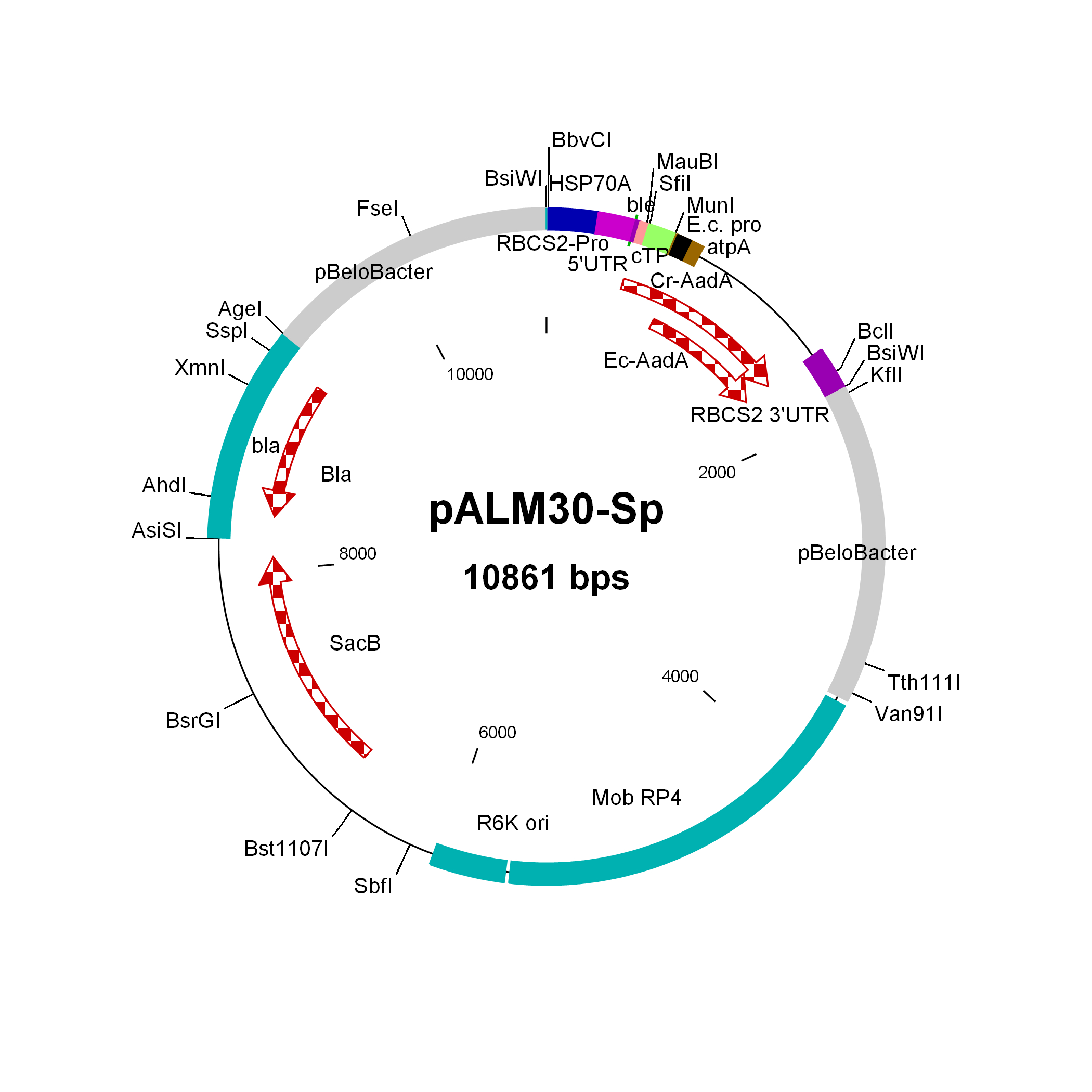
pALM30-Sp
$30.00
$30.00
Source: Olivier Vallon, Institut de Biologie Physico-Chimique, Paris, November 2011
Used to modify Chlamydomonas genomic BACs to Sp resistance
Insert: CrSpAadA (AR promoter, RBCS2 3′-UTR)
Origin: pCVD442 with IS1 and CmR removed (NdeI AsiSI) and replaced by bla, then inserting 3 kbp of pBeloBAC11-Nit8 (AscI AgeI), then inserting (FseI) the CrEcAadA marker from pALM33
Vector: R6K
Host strain: S17-1 λpir
Ap Sp resistant
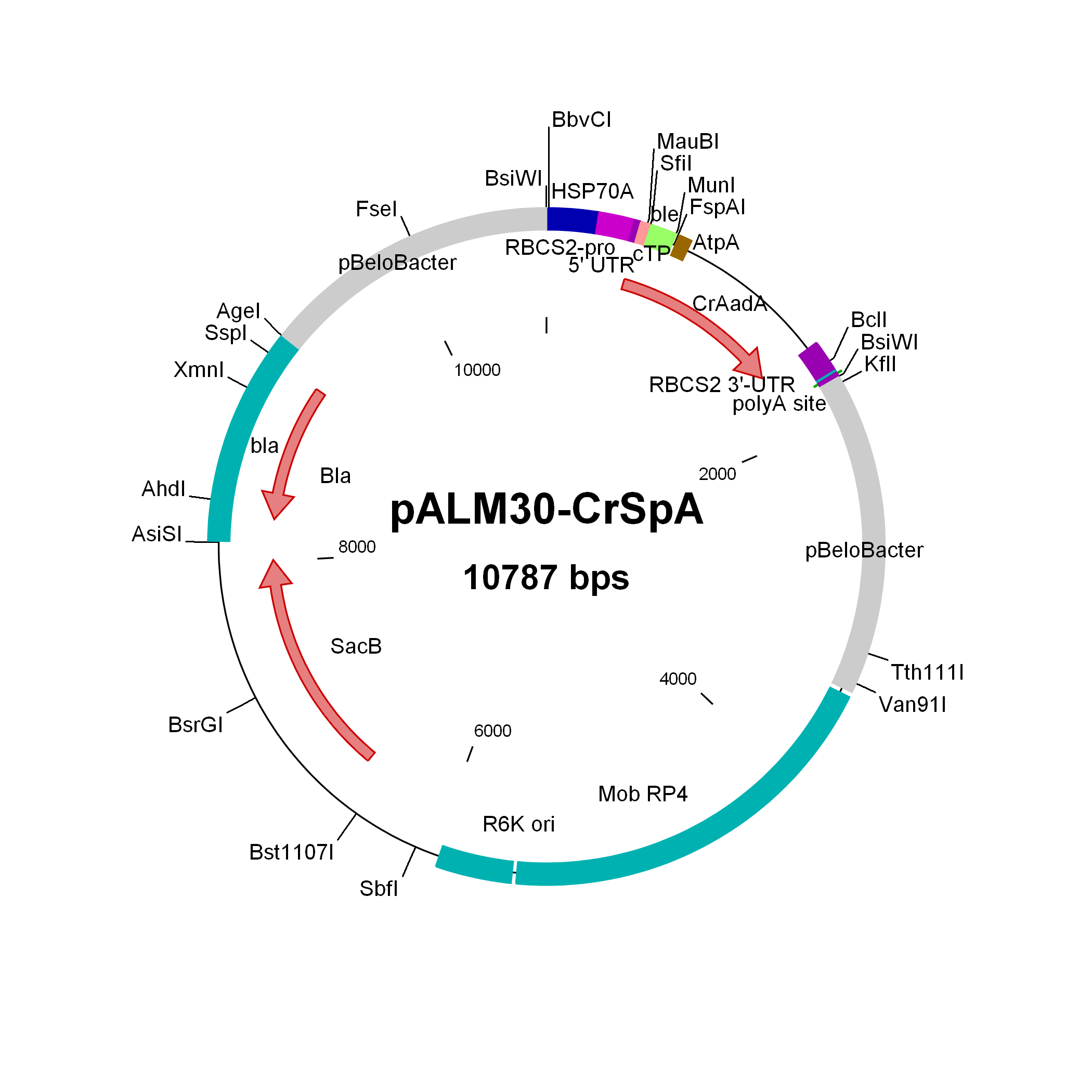
pALM30-CrSpA
$30.00
$30.00
Source: Olivier Vallon, Institut de Biologie Physico-Chimique, Paris, November 2011
Used to modify Chlamydomonas genomic BACs to Sp resistance
Insert: CrAadA (AR promoter, RBCS2 3′-UTR)
Origin: pCVD442 with IS1 and CmR removed (NdeI AsiSI) and replaced by bla, then inserting 3 kbp of pBeloBAC11-Nit8 (AscI AgeI), then inserting (FseI) the CrAadA marker from pALM32 (sense with NIT8)
Vector: R6K
Host strain: S17-1 λpir
Amp resistant
- «Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- …
- 15
- Next Page»