Plasmids
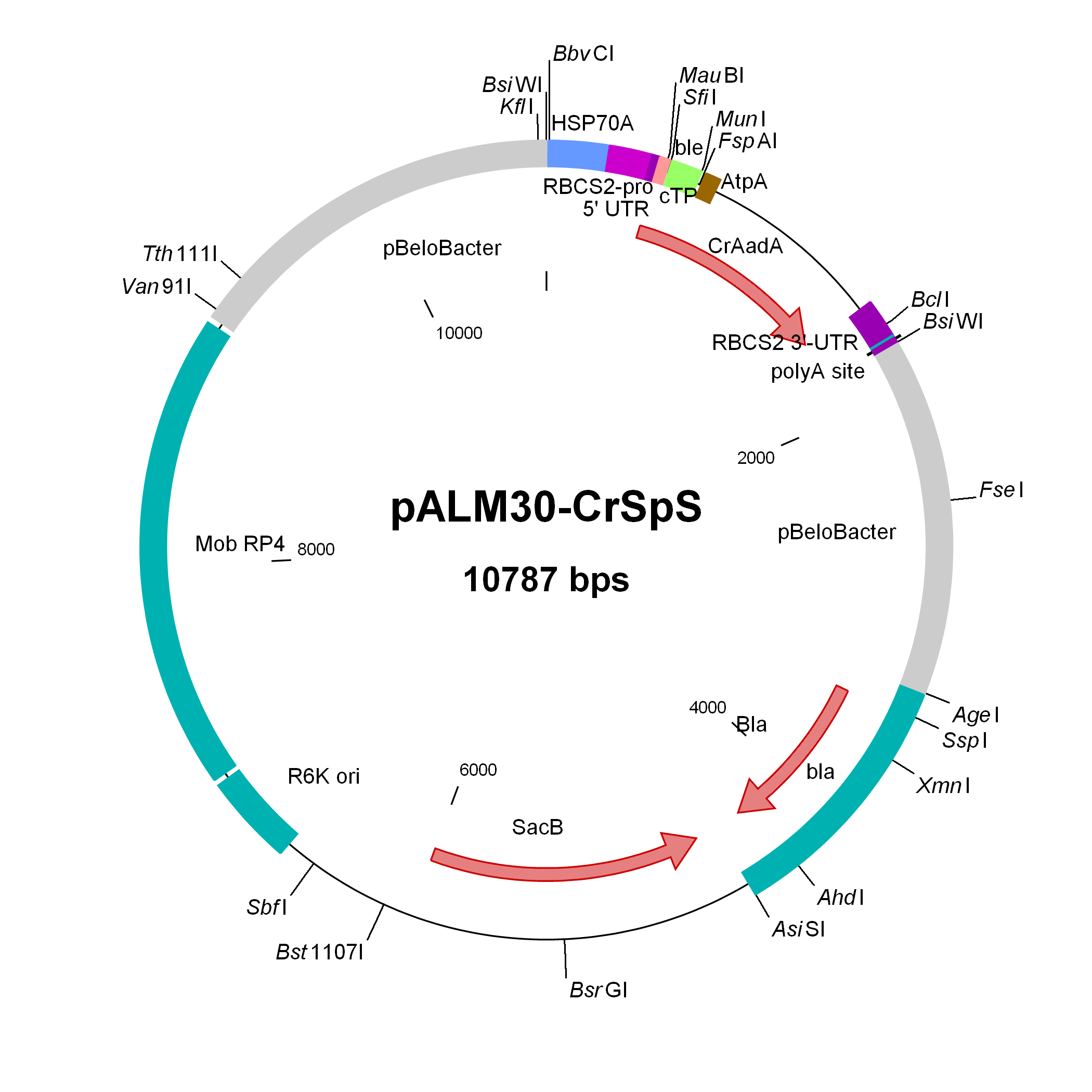
pALM30-CrSpS
$30.00
$30.00
Source: Olivier Vallon, Institut de Biologie Physico-Chimique, Paris, November 2011
Used to modify Chlamydomonas genomic BACs to Sp resistance
Insert: CrAadA (AR promoter, RBCS2 3′-UTR)
Origin: pCVD442 with IS1 and CmR removed (NdeI AsiSI) and replaced by bla, then inserting 3 kbp of pBeloBAC11-Nit8 (AscI AgeI), then inserting (FseI) the CrAadA marker from pALM32 (antisense with NIT8)
Vector: R6K
Host strain: S17-1 λpir
Amp resistant
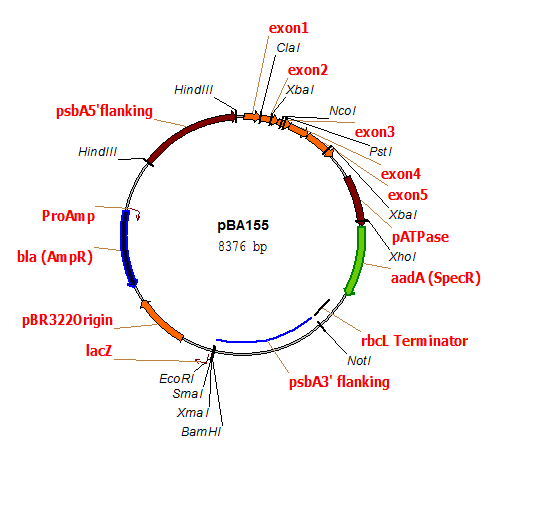
pBA155
$30.00
$30.00
From Richard Sayre via Mustapha Samrakandi, New Mexico Consortium Biolabs, July 2012
Chloroplast transformation plasmid containing bacterial aadA gene conferring spectinomycin (spe-r) resistance inserted downstream of an intron-free psbA gene.
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Minagawa J, Crofts AR (1994) A robust protocol for site-directed mutagenesis of the D1 protein inChlamydomonas reinhardtii: A PCR-splicedpsbA gene in a plasmid conferring spectinomycin resistance was introduced into apsbA deletion strain. Photosynthesis Research 42:121-131
atpX-rluc
$30.00
$30.00
From David Herrin, University of Texas at Austin, October 2012
Luciferase reporter for chloroplast gene expression
Minko I, Holloway SP, Nikaido S, Carter M, Odom OW, Johnson CH, Herrin DL (1999) Renilla luciferase as a vital reporter for chloroplast gene expression in Chlamydomonas. Mol Gen Genet 262:421-425
pSP105 ble cassette
$30.00
$30.00
From Saul Purton, University College London, November 2012
ble (phleomycin resistance gene from S. hindustanus) flanked by RBCS2 5′ and 3′
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Stevens DR, Rochaix JD, Purton S (1996) The bacterial phleomycin resistance gene ble as a dominant selectable marker in Chlamydomonas. Mol Gen Genet 251:23-30
pMN100
$30.00
$30.00
From Pete Lefebvre, U of MN, January 2013
pGEX-4T-2
$30.00
$30.00
From Pete Lefebvre, U of MN, January 2013
pGEX no UTR
$30.00
$30.00
From Pete Lefebvre, U of MN, January 2013
p7.4Xho1HSP70A
$30.00
$30.00
From Carolyn Silflow, U of MN, February 2013
The plasmid insert is a 7.4 kb XhoI fragment from chromosome 8:2,515,636 – 2,523,041.
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Silflow CD, Sun X, Haas NA, Foley JW, Lefebvre PA (2011) The Hsp70 and Hsp40 chaperones influence microtubule stability in Chlamydomonas. Genetics 189:1249-60
pBC1
$30.00
$30.00
From Marilyn Kobayashi, Niyogi lab, March 2013
pBC1 was generated by digestion of pSL18, which contains the aphVIII cassette conferring paromomycin resistance, with XhoI and NotI to remove the PSAD promoter and 3’UTR. This region was replaced with an XhoI/NotI fragment containing the multiple cloning site from pBlueScript II.
amp resistant
pSlip2-1
$30.00
$30.00
pSlip2-2
$30.00
$30.00
pSlip2-4
$30.00
$30.00
p699
$30.00
$30.00
bld1 cDNA
$30.00
$30.00
bld1 cDNA+GFP
$30.00
$30.00
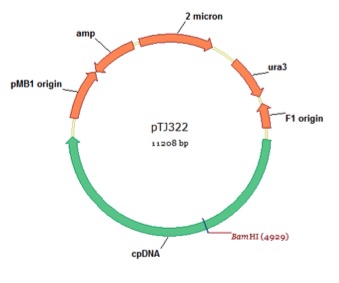
pTJ322
$30.00
$30.00
From Azadeh Pourmir, Johannes Lab, University of Tulsa, August 2013
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Noor-Mohammadi S, Pourmir A, Johannes TW (2012) Method to assemble and integrate biochemical pathways into the chloroplast genome of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biotechnol Bioeng 109:2896-903
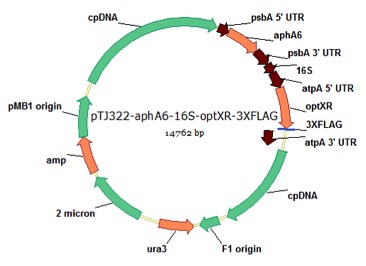
pTJ322-16S/atpA-optXR
$30.00
$30.00
From Azadeh Pourmir, Johannes Lab, University of Tulsa, 8/29/13
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Pourmir A, Noor-Mohammadi S, Johannes TW (2013) Production of xylitol by recombinant microalgae. J Biotechnol 165:178-83
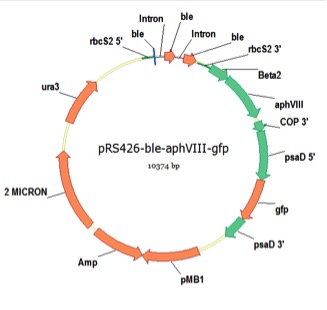
pRS426-ble-aphVIII-gfp
$30.00
$30.00
From Azadeh Pourmir, Johannes Lab, University of Tulsa, August 2013
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
pMJ013b
$30.00
$30.00
From Martin Jonikas, Carnegie Institution for Science, Department of Plant Biology, Stanford, March 2014
This plasmid contains a PsaD promoter driving codon-optimized AphVIII, followed by a CYTc6 intron and PsaD 3’UTR. Digestion with MlyI yields a 2660bp fragment for transformation.
host strain: One Shot® TOP10 E. coli
amp resistant
Zhang R, Patena W, Armbruster U, Gang SS, Blum SR, Jonikas MC (2014) High-throughput genotyping of green algal mutants reveals random distribution of mutagenic insertion sites and endonucleolytic cleavage of transforming DNA. Plant Cell 26:1398-1409
pGlyR1
$30.00
$30.00
From Don Weeks, University of Nebraska, May 2014
Plasmid conferring glyphosate resistance via herbicide resistant GAT gene that can be used as a dominant selectable marker for Chlamydomonas transformations.
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Bruggeman AJ, Kuehler D, Weeks DP (2014) Evaluation of three herbicide resistance genes for use in genetic transformations and for potential crop protection in algae production. Plant Biotechnol J 12:894-902
pOxR2
$30.00
$30.00
From Don Weeks, University of Nebraska, May 2014
Plasmid conferring oxadiazon/oxyfluorfen resistance via herbicide resistant protox rs-3 gene that can be used as a dominant selectable marker for Chlamydomonas transformations.
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Bruggeman AJ, Kuehler D, Weeks DP (2014) Evaluation of three herbicide resistance genes for use in genetic transformations and for potential crop protection in algae production. Plant Biotechnol J 12:894-902
pNorR1
$30.00
$30.00
From Don Weeks, University of Nebraska, May 2014
Plasmid conferring norflurazon resistance via herbicide resistant PDS (R268T) gene that can be used as a dominant selectable marker for Chlamydomonas transformations.
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Bruggeman AJ, Kuehler D, Weeks DP (2014) Evaluation of three herbicide resistance genes for use in genetic transformations and for potential crop protection in algae production. Plant Biotechnol J 12:894-902
pHR15
$30.00
$30.00
From Elizabeth Specht, Stephen Mayfield Lab, University of California San Diego, May 2014
This plasmid is useful for transforming the Chlamydomonas nuclear genome with the reporter ARS2, the periplasmic arylsulfatase, for constitutive expression. The paromomycin resistance eliminates the need to co-transform with another plasmid for selection. The plasmid exhibits greater transformation efficiency and stronger arylsulfatase signal than plasmids with the genomic ARS2 fragment. It is similar to pHR16 but produces slightly lower levels of arylsulfatase expression.
The ARS2 coding sequence and the ARS2 3’ UTR were amplified from a cDNA preparation from a sulfur-starved Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain CC-1010 culture. The selection cassette (PSAD:Paro:PSAD) was inserted upstream of the ARS2 cassette, using blunt restriction/ligation.
Insert: PSAD promoter/5’ UTR:paromomycin resistance (aphVIII):PSAD 3’ UTR immediately upstream of HSP70/RbcS2 promoter/5’ UTR:ARS2 coding sequence:ARS2 3’ UTR
Total insert size is 5,276 bp.
Selection: Ampicillin resistant in E. coli; paromomycin resistant in Chlamydomonas
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
pHR16
$30.00
$30.00
From Elizabeth Specht, Stephen Mayfield Lab, University of California San Diego, May 2014
This plasmid is useful for transforming the Chlamydomonas nuclear genome with the reporter ARS2, the periplasmic arylsulfatase, for constitutive expression. The paromomycin resistance eliminates the need to co-transform with another plasmid for selection. The plasmid exhibits greater transformation efficiency and stronger arylsulfatase signal than plasmids with the genomic ARS2 fragment. It is similar to pHR15 but exhibits higher signal strength in most clones.
The ARS2 coding sequence and the ARS2 3’ UTR were amplified from a cDNA preparation from a sulfur-starved Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain CC-1010 culture. The ARG7 promoter and 5’ UTR were amplified from another cDNA from non-stressed Chlamydomonas reinhardtii strain CC-1010 culture. The selection cassette (PSAD:Paro:PSAD) was inserted upstream of the ARS2 cassette, using blunt restriction/ligation.
Insert: PSAD promoter/5’ UTR:paromomycin resistance (aphVIII):PSAD 3’ UTR immediately upstream of ARG7 promoter/5’ UTR:ARS2 coding sequence:ARS2 3’ UTR
Total insert size is 6,028 bp.
Selection: Ampicillin resistant in E. coli; paromomycin resistant in Chlamydomonas
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
NIT2 genomic pMN68
$30.00
$30.00
From Pete Lefebvre, University of Minnesota, 20 May 2014
host strain: DH5α
amp resistant
Schnell RA, Lefebvre PA (1993) Isolation of the Chlamydomonas regulatory gene NIT2 by transposon tagging. Genetics 134:737-47
pOpt_mVenus_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061060
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mVenus (YFP variant) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_mCerulean3_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061061
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mCerulean3 (a CFP variant) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_gLuc_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061059
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the gLuc (Gaussia princeps luciferase) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_mRuby2_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061063
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert: pOptimized template vector containing the mRuby2 (RFP variant) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
pOpt_Clover_Paro
$30.00
$30.00
From Kyle J. Lauersen, Jan H. Mussgnug, Olaf Kruse, Center for Biotechnology (CeBiTec), Bielefeld University, Germany, June 2014
NCBI accession number: KM061062
Vector: pBluescript backbone, pOptimized synthetic Chlamydomonas expression cassettes
Origin: synthetic construct (DNA synthesis and cloning)
Insert pOptimized template vector containing the Clover (a GFP variant) reporter expression cassette and an antibiotic selection marker expression cassette. Both cassettes contain the HSP70A-RBCS2-InI promoter and RBCS2 3’UTR surrounding either the reporter or the marker. Each reporter contains intron 2 of RBCS2 within its nuclear sequence. Selection marker for Chlamydomonas is paromomycin resistance aphVIII (Sizova et al. 2001).
Host strain: DH5α
Selection: Ampicillin resistance for E. coli culture
Comment: Please follow naming convention for derivative vectors using underscores between new added elements.
Individual annotated vector maps are available in ApE format.
Lauersen KJ, Kruse O, Mussgnug JH (2015) Targeted expression of nuclear transgenes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii with a versatile, modular vector toolkit. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. Jan 15 Lumbreras V, Purton S (1998) Recent advances in chlamydomonas transgenics. Protist 149:23-7 Berthold P, Schmitt R, Mages W (2002) An engineered Streptomyces hygroscopicus aph 7" gene mediates dominant resistance against hygromycin B in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Protist 153:401-12 Sizova I, Fuhrmann M, Hegemann P (2001) A Streptomyces rimosus aphVIII gene coding for a new type phosphotransferase provides stable antibiotic resistance to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene 77:221-9
- «Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- …
- 15
- Next Page»